Page 45 - Linguistically Diverse Educational Contexts
P. 45
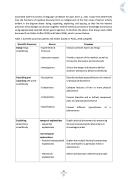
associated with the process of language use (Meyer & Coyle, 2017, p. 212). It was then determined how the functions of cognitive discourse form an integral part of the four areas of learner activity evident in the diagram above: doing, organising, explaining, and arguing, as they link the internal processes of knowledge construction together with the external processes of knowledge transmission using appropriately selected literary genres (genres). To illustrate the above, Graz Group used a table borrowed from Dalton-Puffer (2015) and Polias (2016), which I present below:
Table 1. Scientific processes, genres and modes (based on Polias, 2016, adapted)
Scientific Processes
Genres
Purposes
Doing things scientifically
- Experiments & Protocols
- Laboratory reports
- Investigations
Instruct someone how to do things
Provide a recount of the method, as well as the results, discussions and conclusions
Set out the design and decisions behind students’ attempts to behave scientifically
Describing and organising the world scientifically
- Descriptions
-Comparisons
- Compositions
- Classifications
Describe multiple aspects/features of a natural or physical phenomenon
Compare features of two or more physical phenomena
Present (describe and or define) component parts of a physical phenomenon
Present different types/classes of a phenomenon
Explaining
phenomena scientifically
temporal explanations
- sequential explanations
non-temporal explanations
- factorial/consequential
explanations
- theoretical explanations
Explain physical phenomena by presenting the events producing the phenomena in chronological order
Explain the multiple factors/consequences that contribute to a particular event or phenomenon
Define and illustrate a theoretical principle
30